Table of Contents
Seq2Seq 모델의 등장 배경
- Seq2Seq 모델은 입력과 출력의 길이가 가변적인 경우 사용할 수 있는 모델이다
- 원래도 RNN 계열의 모델이 있었지만, RNN 모델은 입력의 길이와 출력의 길이의 관계가 서로 독립적이지 않다. 출력의 길이를 늘리고 싶으면 그만큼 입력에는 패딩을 붙여야 하는 등의 작업이 필요했고, 이러한 작업을 하더라도 성능이 떨어졌기 때문에, 분명한 한계점을 가지고 있었다
Seq2Seq 모델
- 2014년 구글에서 발표한 Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks 논문에서 제안한 모델이다
- Seq2Seq 모델은 2개의 RNN 계열 모델(논문에서는 LSTM)을 각각 인코더/디코더로 사용해 가변적인 입/출력을 처리한다
- 입력과 출력의 시퀀스 길이가 서로 자유롭기 때문에 서로 다른 도메인의 시퀀스를 출력할 수 있다 (ex. 한국어 -> 영어)
- Seq2Seq 모델은 기계 번역 분야에 많이 사용되며, 그 외에 텍스트 요약, 챗봇 같은 분야에서도 사용할 수 있다
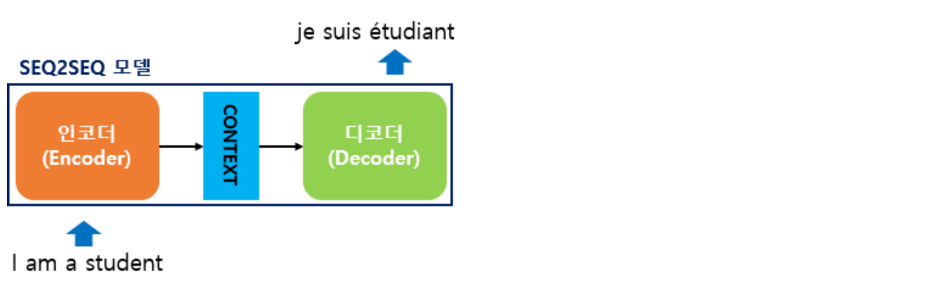
인코더
-
입력 문장의 모든 단어들을 순차적으로 입력받은 뒤에 마지막에 이 모든 단어 정보들을 압축해서 하나의 벡터로 만드는데, 이를 컨텍스트 벡터(context vector)라고 합니다. 입력 문장의 정보가 하나의 컨텍스트 벡터로 모두 압축되면 인코더는 컨텍스트 벡터를 디코더로 전송합니다. 디코더는 컨텍스트 벡터를 받아서 번역된 단어를 한 개씩 순차적으로 출력합니다
-
인코더 아키텍처와 디코더 아키텍처의 내부는 사실 두 개의 RNN 아키텍처 입니다. 입력 문장을 받는 RNN 셀을 인코더라고 하고, 출력 문장을 출력하는 RNN 셀을 디코더라고 합니다. 여기서는 인코더의 RNN 셀을 주황색으로, 디코더의 RNN 셀을 초록색으로 표현합니다. 물론, 성능 문제로 인해 실제로는 바닐라 RNN이 아니라 LSTM 셀 또는 GRU 셀들로 구성됩니다
-
컨텍스트 벡터는 사실 인코더에서의 마지막 RNN 셀의 은닉 상태값을 말하는 것이며, 이는 입력 문장의 모든 단어 토큰들의 정보를 요약해서 담고있다고 할 수 있습니다
디코더
- 디코더는 초기 입력으로 문장의 시작을 의미하는 심볼
<sos>가 들어갑니다. 디코더는<sos>가 입력되면, 다음에 등장할 확률이 높은 단어를 예측합니다. 첫번째 시점(time step)의 디코더 RNN 셀은 다음에 등장할 단어로 je를 예측하였습니다. 첫번째 시점의 디코더 RNN 셀은 예측된 단어 je를 다음 시점의 RNN 셀의 입력으로 입력합니다. 그리고 두번째 시점의 디코더 RNN 셀은 입력된 단어 je로부터 다시 다음에 올 단어인 suis를 예측하고, 또 다시 이것을 다음 시점의 RNN 셀의 입력으로 보냅니다. 디코더는 이런 식으로 기본적으로 다음에 올 단어를 예측하고, 그 예측한 단어를 다음 시점의 RNN 셀의 입력으로 넣는 행위를 반복합니다. 이 행위는 문장의 끝을 의미하는 심볼인<eos>가 다음 단어로 예측될 때까지 반복됩니다. 지금 설명하는 것은 테스트 과정 동안의 이야기입니다. - 훈련 과정에서는 디코더에게 인코더가 보낸 컨텍스트 벡터와 실제 정답인 상황인
<sos>je suis étudiant를 입력 받았을 때, je suis étudiant<eos>가 나와야 된다고 정답을 알려주면서 훈련합니다. 이에 대해서는 뒤에 교사 강요(teacher forcing) 를 설명하면서 재언급하겠습니다. 반면 테스트 과정에서는 앞서 설명한 과정과 같이 디코더는 오직 컨텍스트 벡터와<sos>만을 입력으로 받은 후에 다음에 올 단어를 예측하고, 그 단어를 다음 시점의 RNN 셀의 입력으로 넣는 행위를 반복합니다.
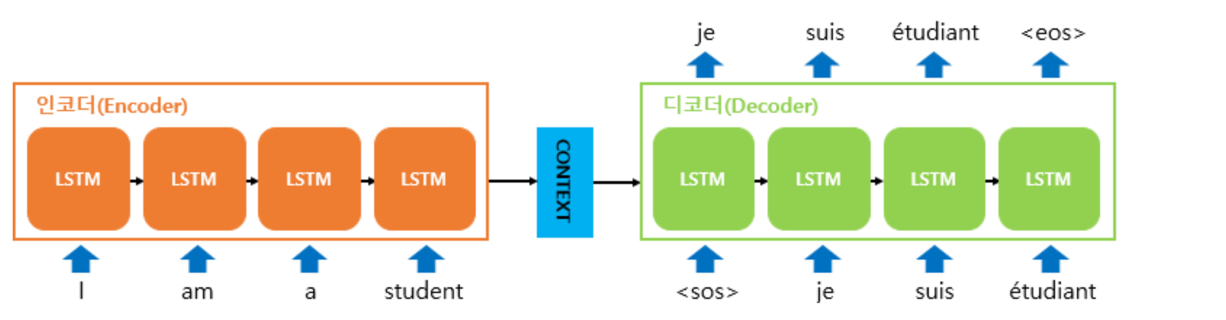
- 컨텍스트 벡터를 디코더의 초기 은닉 상태로만 사용할 수도 있고, 거기서 더 나아가 컨텍스트 벡터를 디코더가 단어를 예측하는 매 시점마다 하나의 입력으로 사용할 수도 있으며 거기서 더 나아가면 어텐션 메커니즘이라는 방법을 통해 지금 알고있는 컨텍스트 벡터보다 더욱 문맥을 반영할 수 있는 컨텍스트 벡터를 구하여 매 시점마다 하나의 입력으로 사용할 수도 있습니다.
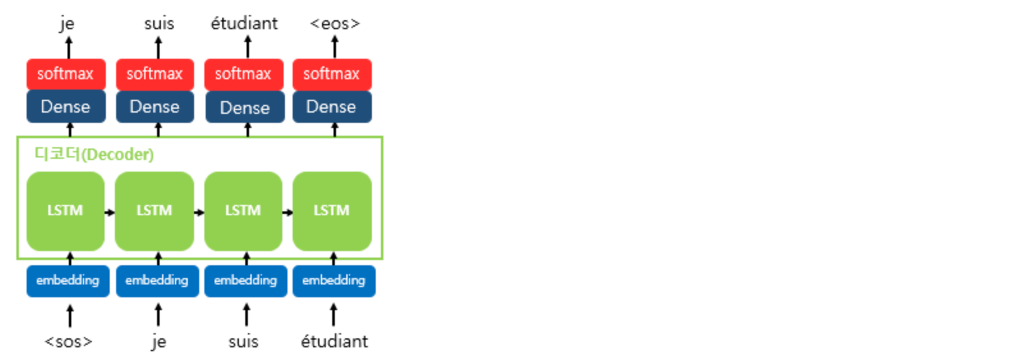
임베딩
- 기계는 텍스트보다 숫자를 잘 처리합니다. 자연어 처리에서 텍스트를 벡터로 바꾸는 방법으로 주로 워드 임베딩이 사용된다고 설명한 바 있습니다. 즉, seq2seq에서 사용되는 모든 단어들은 임베딩 벡터로 변환 후 입력으로 사용됩니다.
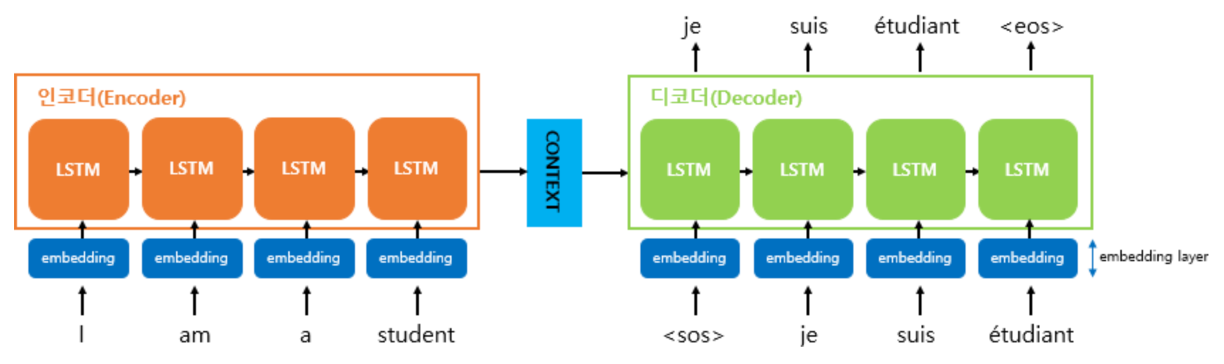
학습
-
모델을 설계하기 전에 혹시 의아한 점은 없으신가요? 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 입력은 오직 이전 디코더 셀의 출력을 입력으로 받는다고 설명하였는데 decoder_input이 왜 필요할까요?
-
훈련 과정에서는 이전 시점의 디코더 셀의 출력을 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 입력으로 넣어주지 않고, 이전 시점의 실제값을 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 입력값으로 하는 방법을 사용할 겁니다. 그 이유는 이전 시점의 디코더 셀의 예측이 틀렸는데 이를 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 입력으로 사용하면 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 예측도 잘못될 가능성이 높고 이는 연쇄 작용으로 디코더 전체의 예측을 어렵게 합니다. 이런 상황이 반복되면 훈련 시간이 느려집니다. 만약 이 상황을 원하지 않는다면 이전 시점의 디코더 셀의 예측값 대신 실제값을 현재 시점의 디코더 셀의 입력으로 사용하는 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이와 같이 RNN의 모든 시점에 대해서 이전 시점의 예측값 대신 실제값을 입력으로 주는 방법을 교사 강요라고 합니다.
한계점
- 고정된 크기의 벡터에 모든 입력 정보를 담아내기 힘들다
- RNN의 문제점인 Gradient Vanishing Problem
Seq2Seq 로 만든 기계 번역 모델
import os, json, re
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from kiwipiepy import Kiwi
디바이스 선택
device = "cpu"
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda:0"
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
device = "mps"
print(device)
데이터 임포트
data_dir_path = "./dataset"
train_data_dir_path = os.path.join(data_dir_path, "train")
valid_data_dir_path = os.path.join(data_dir_path, "valid")
train_data_file = os.path.join(train_data_dir_path, "train.json")
valid_data_file = os.path.join(valid_data_dir_path, "valid.json")
with open(valid_data_file, "r") as f:
json_data = json.load(f)
validation_dataset = json_data['data']
with open(train_data_file, "r") as f:
json_data = json.load(f)
train_dataset = json_data['data']
훈련용 코퍼스, 검증용 코퍼스
train_korean_corpus = []
train_english_corpus = []
for data in train_dataset:
train_korean_corpus.append(data['ko'])
train_english_corpus.append(data['en'])
valid_korean_corpus = []
valid_english_corpus = []
for data in validation_dataset:
valid_korean_corpus.append(data['ko'])
valid_english_corpus.append(data['en'])
train_korean_corpus = train_korean_corpus[:50000]
valid_korean_corpus = valid_korean_corpus[:1000]
train_english_corpus = train_english_corpus[:50000]
valid_english_corpus = valid_english_corpus[:1000]
한국어 데이터 토큰화
kiwi = Kiwi()
korean_vocab = set()
train_korean_tokenized_data = []
valid_korean_tokenized_data = []
train_korean_tokenized_idx_data = []
valid_korean_tokenized_idx_data = []
for sentence in train_korean_corpus:
tokenized_res = kiwi.analyze(sentence)
tokenized_res = tokenized_res[0][0]
tokenized_sentence_list = []
for token in tokenized_res:
token_text = token[0]
if not token_text == '>':
korean_vocab.add(token_text)
tokenized_sentence_list.append(token_text)
train_korean_tokenized_data.append(tokenized_sentence_list)
for sentence in valid_korean_corpus:
tokenized_res = kiwi.analyze(sentence)
tokenized_res = tokenized_res[0][0]
tokenized_sentence_list = []
for token in tokenized_res:
token_text = token[0]
if not token_text == '>':
korean_vocab.add(token_text)
tokenized_sentence_list.append(token_text)
valid_korean_tokenized_data.append(tokenized_sentence_list)
korean_idx_token_dict = dict()
korean_token_idx_dict = dict()
for idx, token in enumerate(list(korean_vocab)):
korean_idx_token_dict[idx] = token
korean_token_idx_dict[token] = idx
assert len(korean_vocab) == len(korean_idx_token_dict)
assert len(korean_vocab) == len(korean_token_idx_dict)
for tokenized_sentence in train_korean_tokenized_data:
tokenized_ids = []
for tokenized_word in tokenized_sentence:
tokenized_ids.append(korean_token_idx_dict[tokenized_word])
train_korean_tokenized_idx_data.append(tokenized_ids)
for tokenized_sentence in valid_korean_tokenized_data:
tokenized_ids = []
for tokenized_word in tokenized_sentence:
tokenized_ids.append(korean_token_idx_dict[tokenized_word])
valid_korean_tokenized_idx_data.append(tokenized_ids)
영어 데이터 토큰화
english_vocab = set()
train_english_tokenized_data = []
valid_english_tokenized_data = []
train_english_tokenized_idx_data = []
valid_english_tokenized_idx_data = []
for sentence in train_english_corpus:
sentence = re.sub(pattern=r'\b([A-Za-z]+)\b', repl=' \\1 ',string=sentence)
sentence = re.sub(pattern=r'[\s]+', repl=' ', string=sentence)
tokenized_sentence_list = []
for token_text in sentence.split():
if not token_text == '>':
english_vocab.add(token_text)
tokenized_sentence_list.append(token_text)
train_english_tokenized_data.append(tokenized_sentence_list)
for sentence in valid_english_corpus:
sentence = re.sub(pattern=r'\b([A-Za-z]+)\b', repl=' \\1 ',string=sentence)
sentence = re.sub(pattern=r'[\s]+', repl=' ', string=sentence)
tokenized_sentence_list = []
for token_text in sentence.split():
if not token_text == '>':
english_vocab.add(token_text)
tokenized_sentence_list.append(token_text)
valid_english_tokenized_data.append(tokenized_sentence_list)
english_idx_token_dict = dict()
english_token_idx_dict = dict()
for idx, token in enumerate(list(english_vocab), 2): # 0과 1에는 각각 <sos>, <eos> 넣을 예정
english_idx_token_dict[idx] = token
english_token_idx_dict[token] = idx
english_vocab.add('<sos>')
english_vocab.add('<eos>')
english_idx_token_dict[0] = '<sos>'
english_idx_token_dict[1] = '<eos>'
english_token_idx_dict['<sos>'] = 0
english_token_idx_dict['<eos>'] = 1
assert len(english_vocab) == len(english_idx_token_dict)
assert english_token_idx_dict['<sos>'] == 0
assert english_token_idx_dict['<eos>'] == 1
assert english_idx_token_dict[0] == '<sos>'
assert english_idx_token_dict[1] == '<eos>'
for tokenized_sentence in train_english_tokenized_data:
tokenized_ids = []
for tokenized_word in tokenized_sentence:
tokenized_ids.append(english_token_idx_dict[tokenized_word])
train_english_tokenized_idx_data.append(tokenized_ids)
for tokenized_sentence in valid_english_tokenized_data:
tokenized_ids = []
for tokenized_word in tokenized_sentence:
tokenized_ids.append(english_token_idx_dict[tokenized_word])
valid_english_tokenized_idx_data.append(tokenized_ids)
훈련/검증용 데이터셋
train_encoder_input_dataset = train_korean_tokenized_idx_data
train_decoder_input_dataset = [[0] + idx_list for idx_list in train_english_tokenized_idx_data]
train_decoder_target_dataset = [idx_list + [1] for idx_list in train_english_tokenized_idx_data]
valid_encoder_input_dataset = valid_korean_tokenized_idx_data
valid_decoder_input_dataset = [[0] + idx_list for idx_list in valid_english_tokenized_idx_data]
valid_decoder_target_dataset = [idx_list + [1] for idx_list in valid_english_tokenized_idx_data]
모델 정의
encoder_vocab_size = len(korean_vocab)
decoder_vocab_size = len(english_vocab)
embedding_size = 256
hidden_size = 512
num_layers = 1
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(encoder_vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=embedding_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers)
def forward(self, x):
embedding_x = self.embedding(x)
output, hidden = self.lstm(embedding_x)
return hidden
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(decoder_vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=embedding_size, hidden_size=hidden_size)
self.output_layer = nn.Linear(hidden_size, decoder_vocab_size)
def forward(self, x, hidden):
embedding_x = self.embedding(x)
output, hidden = self.lstm(embedding_x, hidden)
output = self.output_layer(output)
return output, hidden
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, encoder_input, decoder_input):
encoder_hidden = self.encoder(encoder_input)
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = self.decoder(decoder_input, encoder_hidden)
return decoder_output
encoder = Encoder()
decoder = Decoder()
encoder.to(device)
decoder.to(device)
model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
model.to(device)
criterion.to(device)
훈련
def train():
model.train()
total = 0
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (encoder_input, decoder_input, decoder_target) in enumerate(zip(train_encoder_input_dataset, train_decoder_input_dataset, train_decoder_target_dataset)):
optimizer.zero_grad()
encoder_input = torch.as_tensor(encoder_input).to(device)
decoder_input = torch.as_tensor(decoder_input).to(device)
decoder_target = torch.as_tensor(decoder_target).to(device)
outputs = model(encoder_input, decoder_input)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, decoder_target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total += decoder_target.shape[0]
running_loss += loss.item()
running_corrects += sum(preds == decoder_target)
if i % 2000 == 0:
print('training_running_loss', running_loss / total, ':::', 'training_runing_corrects', (running_corrects / total).item())
print('training_prediction sentence: ', " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[preds_idx] for preds_idx in preds.tolist()]))
print('training_answer sentence: ', " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[preds_idx] for preds_idx in decoder_target.tolist()]))
print(f'train loss: {running_loss / total}, accuracy: {running_corrects / total}')
return running_loss / total, (running_corrects / total).item()
def validate():
model.eval()
total = 0
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (encoder_input, decoder_input, decoder_target) in enumerate(zip(valid_encoder_input_dataset, valid_decoder_input_dataset, valid_decoder_target_dataset)):
encoder_input = torch.as_tensor(encoder_input).to(device)
decoder_input = torch.as_tensor(decoder_input).to(device)
decoder_target = torch.as_tensor(decoder_target).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(encoder_input, decoder_input)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, decoder_target)
total += decoder_target.shape[0]
running_loss += loss.item()
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == decoder_target.data)
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('validation_running_loss', running_loss / total, ':::', 'valid_runing_corrects', (running_corrects / total).item())
print('validation_prediction sentence: ', " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[preds_idx] for preds_idx in preds.tolist()]))
print('validation_answer sentence: ', " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[preds_idx] for preds_idx in decoder_target.tolist()]))
print(f'val loss: {running_loss / total}, accuracy: {running_corrects / total}')
return running_loss / total, (running_corrects / total).item()
num_epochs = 20
best_val_acc = 0
best_epoch = 0
history = []
accuracy = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print(f'===========================[Epoch: {epoch + 1}===========================')
train_loss, train_acc = train()
val_loss, val_acc = validate()
history.append((train_loss, val_loss))
accuracy.append((train_acc, val_acc))
if val_acc > best_val_acc:
print("[Info] best validation accuracy!")
best_val_acc = val_acc
best_epoch = epoch
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"best_checkpoint_epoch_{epoch + 1}.pth")
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
training_running_loss 0.1323791609870063 ::: training_runing_corrects 0.6666666865348816
training_prediction sentence: If you have to the order you can , please will send the it right away . <eos>
training_answer sentence: If you reply to the color you want , we will start making it right away . <eos>
training_running_loss 0.24309469693665595 ::: training_runing_corrects 0.4238814115524292
training_prediction sentence: I , I hope like to ask you you have send the the as as and of the product . <eos>
training_answer sentence: Also , I would like to ask if you can send me additional ingredient analysis data of the product . <eos>
training_running_loss 0.24536820228284328 ::: training_runing_corrects 0.42408233880996704
training_prediction sentence: How ' the product , right is the problem of ? <eos>
training_answer sentence: Aside from the quality , what is the introduction price ? <eos>
train loss: 0.24543969707713492, accuracy: 0.42317888140678406
validation_running_loss 0.06925033330917359 ::: valid_runing_corrects 1.0
validation_prediction sentence: Oh , really ? <eos>
validation_answer sentence: Oh , really ? <eos>
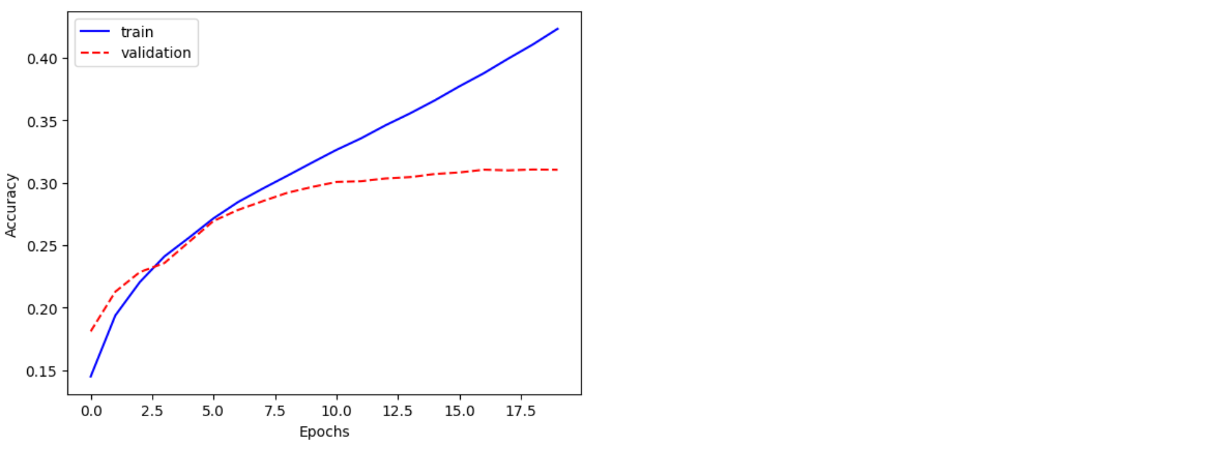
val loss: 0.338049114092056, accuracy: 0.3103710412979126
plt.plot([x[0] for x in accuracy], 'b', label='train')
plt.plot([x[1] for x in accuracy], 'r--',label='validation')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.legend()
추론
class InferenceSeq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder):
super(InferenceSeq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, encoder_input, prev_output): # decoder_input 뺐다 (no teacher-forcing)
encoder_hidden = self.encoder(encoder_input)
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = self.decoder(prev_output, encoder_hidden)
return decoder_output
inference_model = InferenceSeq2Seq(encoder, decoder).to(device)
def inference(test_encoder_input):
stop_condition = False
pred_ids = []
prev_output = torch.LongTensor([0]).to(device)
while len(pred_ids) < 20 and (not stop_condition):
decoder_output = inference_model(test_encoder_input, prev_output)
prev_output = torch.max(decoder_output, 1)[1]
if prev_output.item() == 1:
stop_condition = True
pred_ids.append(prev_output.item())
return pred_ids
for i in [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45]:
test_encoder_input = valid_encoder_input_dataset[i]
test_encoder_input = torch.as_tensor(test_encoder_input).to(device)
pred_ids = inference(test_encoder_input)
print("한글 문장: ", " ".join([korean_idx_token_dict[idx_token] for idx_token in test_encoder_input.tolist()]))
print("정답 번역 문장: ", " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[idx_token] for idx_token in valid_decoder_target_dataset[i]]))
print("모델 번역 문장: ", " ".join([english_idx_token_dict[token_idx] for token_idx in pred_ids]))
print("-------------------------------------------------------")
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 나 가 열 이 얼마나 받 었 겠 니 .
정답 번역 문장: Can you imagine how upset I was ? <eos>
모델 번역 문장: I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 아빠 로서 는 그것 이 좀 화 가 나 ᆯ 수 있 죠 .
정답 번역 문장: As a father , you can be a little angry about it . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: You can I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 오픈 과 동시 에 이벤트 를 진행 하 려고 하 ᆸ니다 .
정답 번역 문장: We are going to hold an event as soon as it opens . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: We would be used to the product I think I think I think I think I think I think I
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 현재 저희 는 짧 은 시간 안 에 폭넓 은 고객 층 에 닿 을 수 있 는 계획 을 세우 고 있 습니다 .
정답 번역 문장: Currently , we are planning to reach a wide range of customers in a short time . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: We have been also also also also also also also also also also also also also also also also also
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 다음 2 개월 까지 계약 이 만료 되 지 않 는 것 으로 알 고 있 습니다 .
정답 번역 문장: I know that the contract won ' t expire until the next two months . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: There are BBB I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 아 그래 .
정답 번역 문장: Oh , okay . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my Oh my
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 에 이 , 무슨 태 가 나 어 .
정답 번역 문장: What are you talking about ? <eos>
모델 번역 문장: It ' s this product I think I think I think I think I think I think I think I
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 드론 은 우리 에게 많 은 도움 이 되 었 습니다 .
정답 번역 문장: The drone helped us out a lot . <eos>
모델 번역 문장: The product made of BBB has been we have been we have been we have been we have been we
-------------------------------------------------------
한글 문장: 평소 에 도 .
정답 번역 문장: Usually .. <eos>
모델 번역 문장: It ' s not it ' s not it ' s not it ' s not it ' s not
-------------------------------------------------------



































![[NLP] Seq2Seq](/images/nlp_logo.png)
