Table of Contents
- JOIN과 SUBQUERY 둘 다 사용할 수 있다면 어떤 것을 쓰는게 좋을까
- LEFT OUTER JOIN을 사용할 때 조건을 만족하는 행이 2개인 경우
- FROM에서 콤마(,)가 사용된 경우
- 날짜 관련 함수
- ROW_NUMBER()
- 윈도우 함수
- OVER()
- CTE(Common Table Expression)
- LEAD, LAG 함수
- 3 NOT IN (null, 1, 2)
- WHERE 조건절에 레코드(튜플) 사용할 수도 있음
- JOIN 쿼리에서 ON절과 WHERE절에 표기하는 것의 차이
- Subset
- Comparing Sets
- INNER JOIN은 ON이 없어도 된다?
- ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), DENSE_RANK()
- 서브쿼리에서는 메인쿼리의 컬럼을 사용할 수 있다
- 컬럼명이 SQL 문법에 포함되는 경우 쌍따옴표로 묶어주면 된다
- UNION 말고 UNION ALL도 있다
- 참고
JOIN과 SUBQUERY 둘 다 사용할 수 있다면 어떤 것을 쓰는게 좋을까
- Sub-query solution
SELECT Name as Employee FROM Employee e
WHERE Salary > (
Select Salary FROM Employee m WHERE m.Id = e.ManagerId
)
Advantages Of Subquery
- Complex query can be broken down into a series of logical steps.
- Subquery is easy to read, understand and maintain.
- It allow to use the results of another query in the outer query.
Disadvantages of Subquery
- Execution is slower than JOIN.
- We cannot modify a table and select from the same table within a subquery in the same SQL statement.
- JOIN solution
SELECT
a.NAME AS Employee
FROM Employee AS a JOIN Employee AS b
ON a.ManagerId = b.Id
AND a.Salary > b.Salary
Advantage of a JOIN
- Execution and retrieval time faster than subqueries.
Disadvantages Of JOIN
- Database server has to do more work when it comes to a lot of joins in a query => more time consuming to retrieve data
- Developer can be confused to choose the appropriate type among many types of joins.
- Conclusion
- Most developers prioritize speed optimizing while others prioritize logic. It ups to you in your specific case.
LEFT OUTER JOIN을 사용할 때 조건을 만족하는 행이 2개인 경우
문제 Consecutive Available Seats
여기서 나는 LEFT OUTER JOIN을 2번 썼다. [현재 좌석, 이전 좌석, 이후 좌석] 이런식으로.
정답은 맞았지만 이렇게 조인을 2번이나 써야하나 라는 생각에 다른 사람들의 풀이를 구경해봤다.
풀이 중에
select distinct a.seat_id
from cinema a
join cinema b
on abs(a.seat_id - b.seat_id) = 1
and a.free=true and b.free=true
order by a.seat_id;
을 봤다. 조인을 1번만 쓰고 있다. 근데 이 방법은 ON절에 사용된 조건이 driving table 행에 조인되는 derived table의 행이 2개가 조인되는 결과를 가져오게 될 것 같았다. 그래서 이러한 경우에는 결과 테이블이 어떻게 될지 궁금해 검색해봤다.
haerong22, LEFT OUTER JOIN 의 함정
위 블로그 내용을 보니
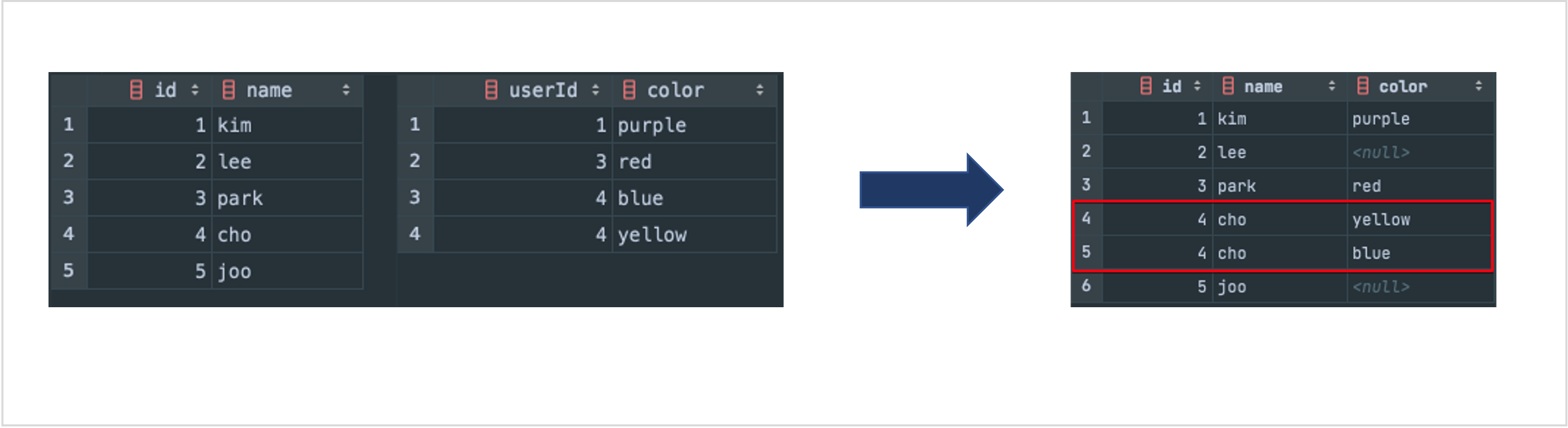
이렇게 id 값이 중복되는 데이터 뻥튀기(?) 현상이 일어났다.
이 때는
- 테이블간 제약 조건을 명확히 한다.
- 조인 조건을 추가
- distinct 사용
- group by 사용
- top 1, limit 사용
와 같은 방법을 이용해 해결할 수 있다. 위의 풀이에서는 distinct를 추가했다.
FROM에서 콤마(,)가 사용된 경우
FROM 절에서 여러 테이블을 함께 사용할 때 사람들마다 쿼리 작성법이 조금씩 달랐다. 표기법의 차이일 뿐 다음은 같은 역할을 한다.
- INNER JOIN = JOIN = ,
- LEFT OUTER JOIN = LEFT JOIN
- RIGHT OUTER JOIN = RIGHT JOIN
날짜 관련 함수
- DATE_SUB()
- INTERVAL
- DATE_FORMAT()
ROW_NUMBER()
- Assigns a sequential integer to every row within its partition
- We will show you how to add a sequential integer to each row or group of rows in the result set.
- ROW_NUMBER() is a window function that returns a sequential number for each row, starting from 1 for the first row.
윈도우 함수
- 특정 범위마다 함수를 적용하는 것을 윈도우 함수라고 함
- MySQL에서 제공하는 윈도우 함수라고 따로 정의해둔 윈도우 함수 묶음이 있음
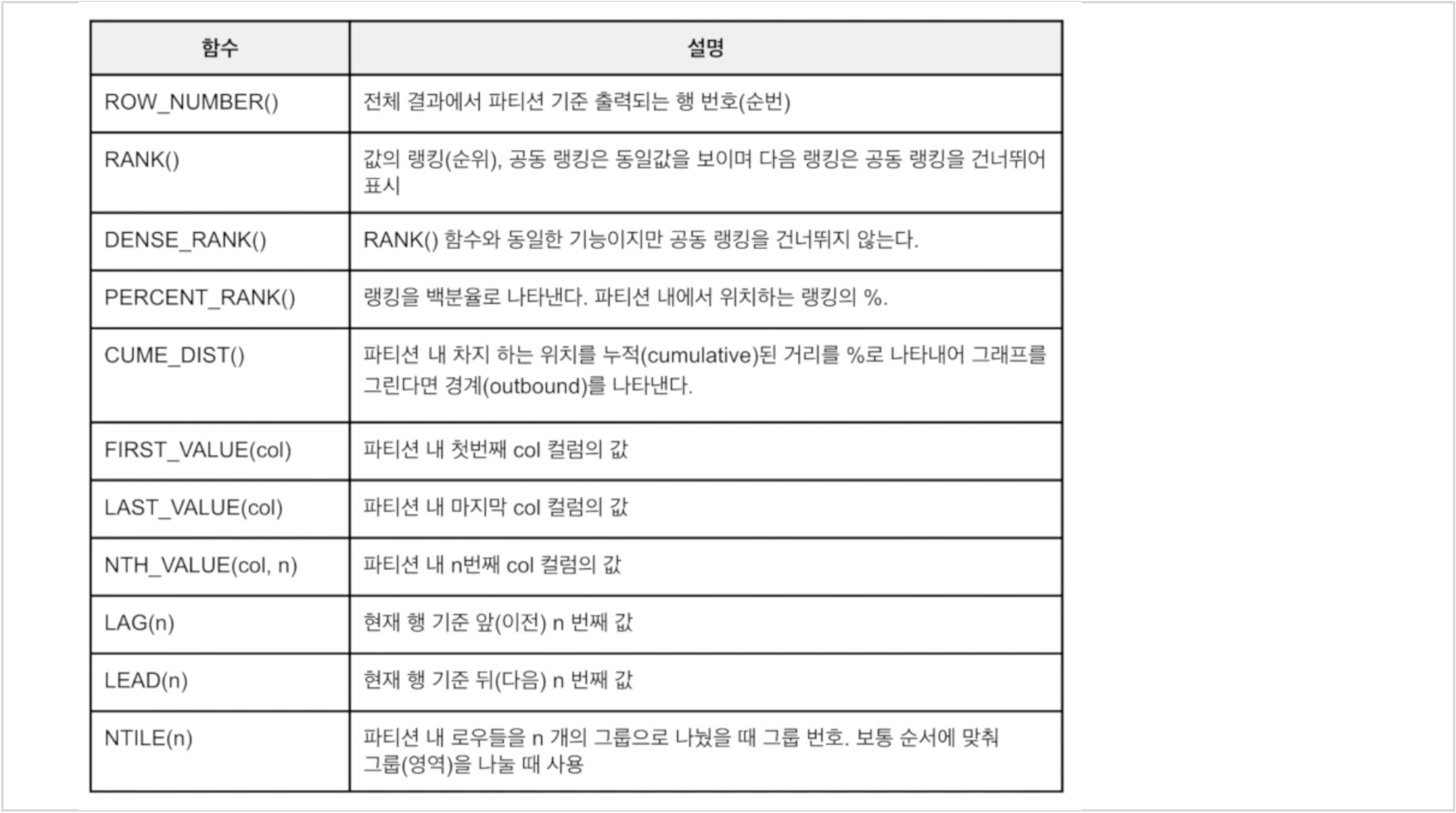
- 집계 함수도 OVER절을 이용해 범위를 정의하면 윈도우 함수로 사용할 수 있음(Most aggregate functions also can be used as window functions, MySQL 공식문서)
- 사용 방법: [윈도우 함수] + [OVER 절] or [집계 함수] + [OVER 절]
- 범위마다 함수를 적용한다는 점에서 GROUP BY와 비슷하게 느껴지지만, GROUP BY는 집계된 결과를 테이블로 보여주는 반면, 윈도우 함수는 집계된 결과를 기존 테이블에 하나의 열로 추가하여 결과를 볼 수 있음
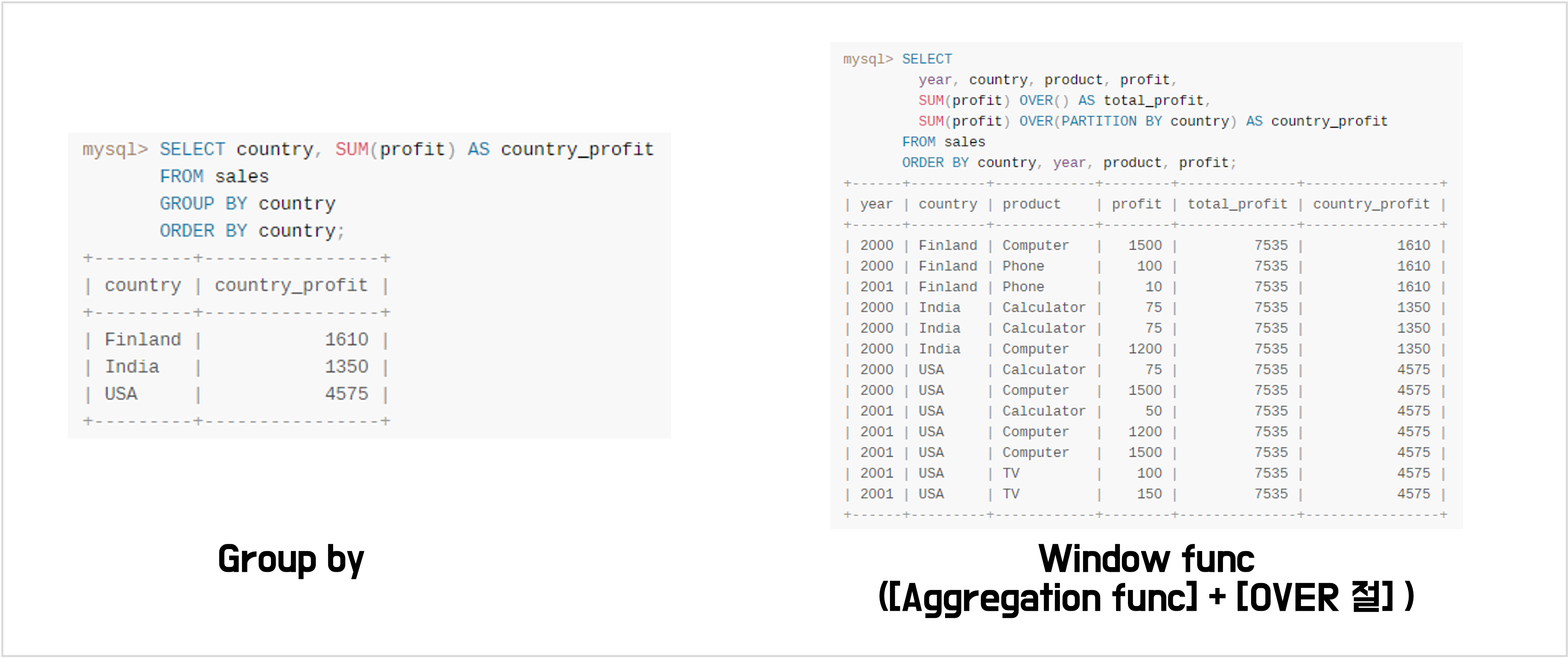
OVER()
- If you want to learn window functions in MySQL, you need to understand the OVER clause
- In 2018, MySQL introduced a new feature: window functions, which are accessed via the OVER clause. Window functions are a super powerful resource available in almost all SQL databases. They perform a specific calculation (e.g. sum, count, average, etc.) on a set of rows; this set of rows is called a “window” and is defined by the MySQL OVER clause.
- OVER clause which has three possible elements: partition definition, order definition, and frame definition.
[window_function(expression)][aggregation_function(expression)] OVER ( [partition_defintion] [order_definition] [frame_definition] ) - PARTITION BY: 윈도우 범위 결정
- ORDER BY: 정렬하여 계산
CTE(Common Table Expression)
- 문제: All People Report to the Given Manager
- In MySQL every query generates a temporary result or relation. In order to give a name to those temporary result set, CTE is used.
- A CTE is defined using WITH clause
- A recursive CTE is a subquery which refer to itself using its own name
- The recursive CTEs are defined using WITH RECURSIVE clause
- There should be a terminating condition to recursive CTE.
- The recursive CTEs are used for series generation and traversal of hierarchical or tree-structured data
WITH RECURSIVE CTE AS (
SELECT employee_id
FROM Employees
WHERE manager_id = 1 AND employee_id != 1
UNION ALL
SELECT e.employee_id
FROM CTE c INNER JOIN Employees e ON c.employee_id = e.manager_id
)
SELECT employee_id
FROM CTE
ORDER BY employee_id
LEAD, LAG 함수
- Non Aggregation Window Function 중 하나
- lead -> 이끌다 -> 현재 행 다음
- lag -> 질질 끌다 -> 현재 행 이전
- LEAD(expr, N, default) OVER(PARTITION BY ~ ORDER BY ~)
3 NOT IN (null, 1, 2)
- Tree Node 문제
- True로 여겨질 줄 알았으나 False였다
WHERE 조건절에 레코드(튜플) 사용할 수도 있음
SELECT student_id, MIN(course_id) AS course_id, grade
FROM Enrollments
WHERE (student_id, grade) IN
(SELECT student_id, MAX(grade)
FROM Enrollments
GROUP BY student_id)
GROUP BY student_id, grade
ORDER BY student_id
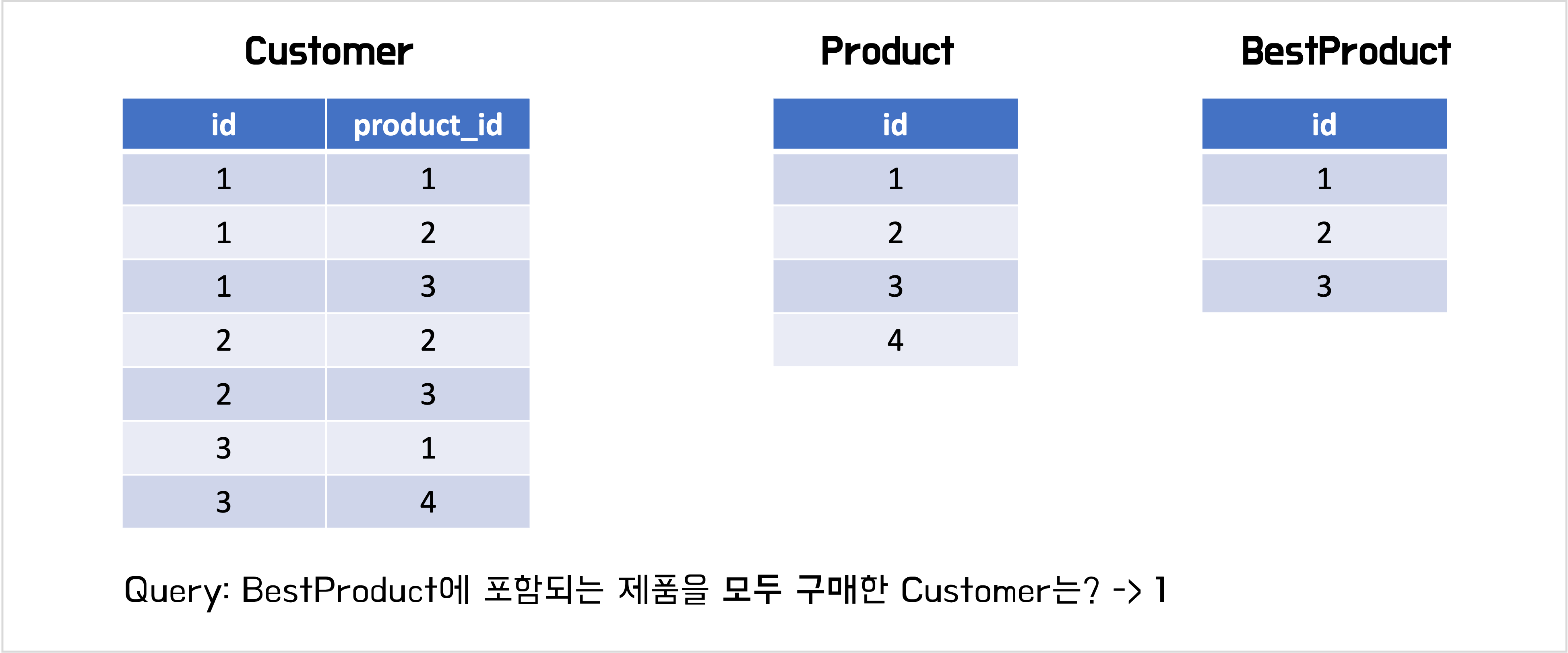
JOIN 쿼리에서 ON절과 WHERE절에 표기하는 것의 차이
Subset
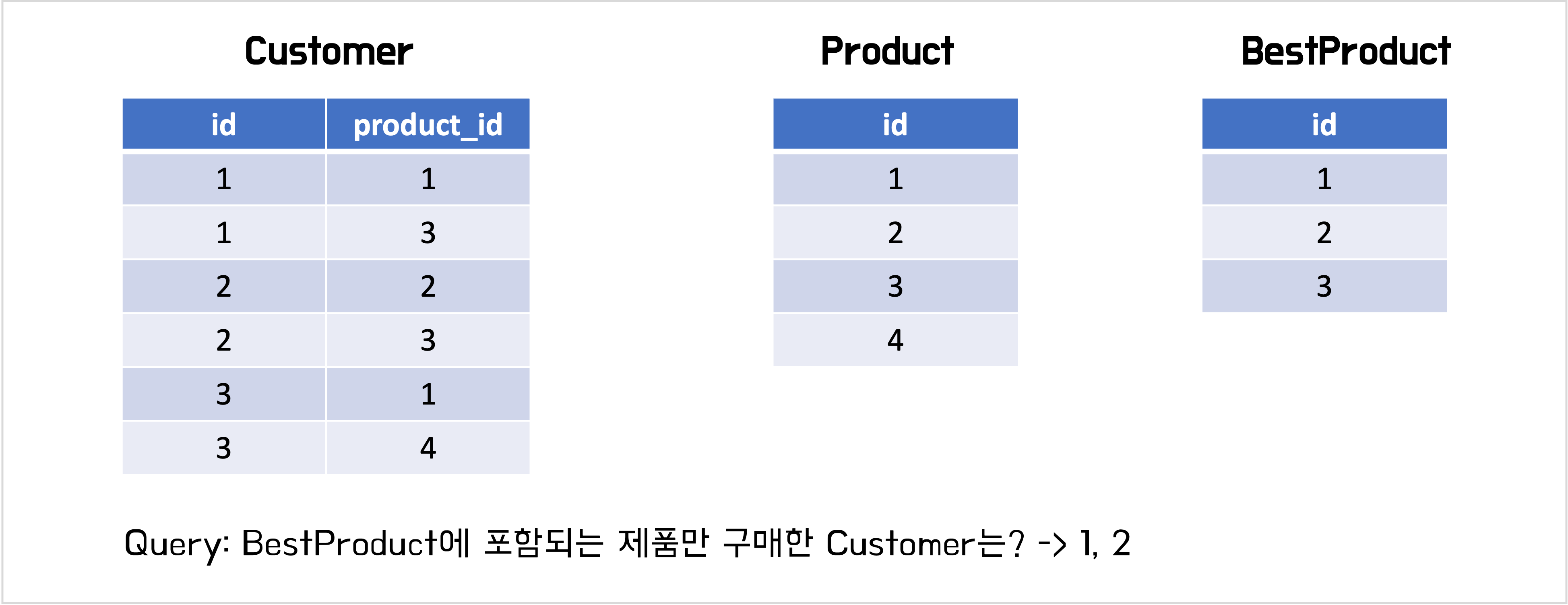
Comparing Sets
INNER JOIN은 ON이 없어도 된다?
- INNER JOIN, JOIN 또는 그냥 콤마(,)를 이용해 두 테이블을 조인할 때는 ON이 없어도 된다
- (OUTER JOIN은 없으면 에러남)
- ON없이 사용하는 경우를 Cartesian Product(곱집합) 이라고 함
- A: {1, 2, 3}, B: {x, y} -> FROM A, B를 하면 -> {[1, x], [1, y], [2, x], [2, y], [3, x], [3, y]}
- 이 개념을 활용하면 LeetCode의 Shortest Distance in a Plane 문제를 풀 수 있다
ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), DENSE_RANK()
| ROW_NUMBER() | 공동 순위를 무시함 (ex: 1,2,3,4 …) |
| RANK() | 공동 순위만큼 건너뜀 (ex: 1,2,2,4 …) |
| DENSE_RANK() | 공동 순위를 뛰어넘지 않음 (ex: 1,2,2,3 …) |
서브쿼리에서는 메인쿼리의 컬럼을 사용할 수 있다
SELECT S1.Score, (
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT Score) FROM Scores WHERE Score >= S1.Score) AS "rank"
FROM Scores S1
ORDER BY S1.Score DESC
컬럼명이 SQL 문법에 포함되는 경우 쌍따옴표로 묶어주면 된다
SELECT
score,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY score) AS "rank"
FROM Scores
UNION 말고 UNION ALL도 있다
{[1, ‘kim’]}과 {[1, ‘kim’]}을 합칠 때
- UNION -> {[1, ‘kim’]}
- UNION ALL -> {[1, ‘kim’], [1, ‘kim’]}
참고
- MySQL tutorial: MySQL ROW_NUMBER, This is How You Emulate It
- SQL OVER 절
- [MySQL] 윈도우함수(Window Function)
- MySQL 공식문서: 12.21.1 Window Function Descriptions
- LearnSQL: What Is the MySQL OVER Clause?
- GeeksforGeeks: MySQL Recursive CTE (Common Table Expressions)
- horang, [MySQL] 계층 쿼리 - WITH, WITH RECURSIVE 사용법



































![[MySQL] SQL을 이용한 데이터 분석에서 겪었던 다양한 경험들](/images/mysql_logo.png)
