Table of Contents
Sharing state between components

- 부모 컴포넌트에서 자식 컴포넌트로 속성을 전달할 수 있다
- 하나의 상태 변수로 두 개의 컴포넌트가 함께 변하도록 하려면, 두 컴포넌트의 공통 부모 컴포넌트에서 상태 변수를 정의하고, 상태 변수를 두 자식 컴포넌트에게 속성(props)으로 전달하면 된다
- Finally, pass the event handlers down so that the children can change the parent’s state.
Passing Data Deeply with Context
- Usually, you will pass information from a parent component to a child component via props
- passing props can become verbose and inconvenient if you have to pass them through many components in the middle, or if many components in your app need the same information.
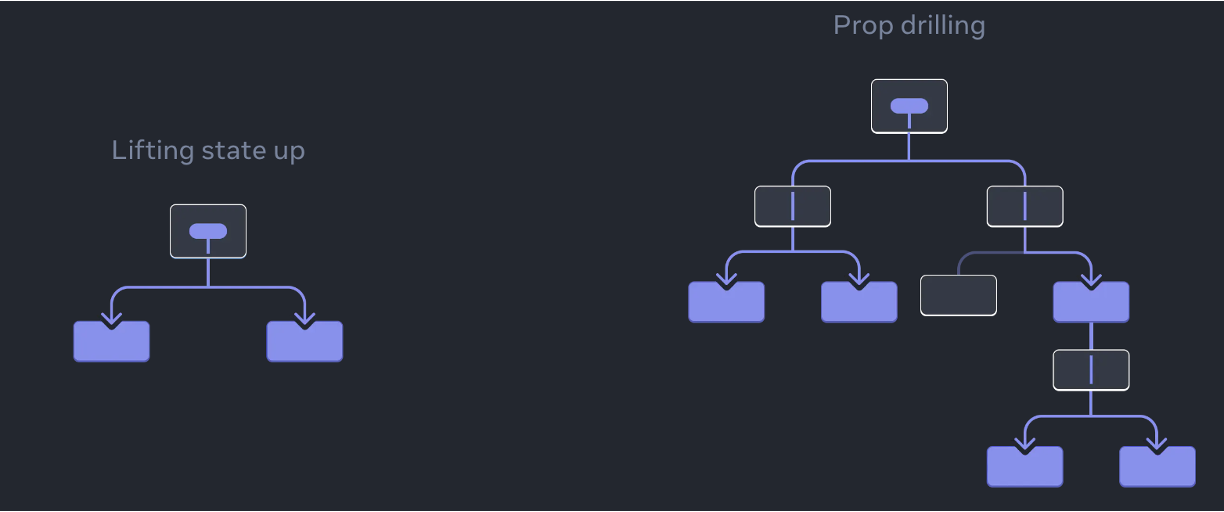
- Context lets the parent component make some information available to any component in the tree below it without passing it explicitly through props

- Context lets a component provide some information to the entire tree below it.
- To pass context:
- Create and export it with export const MyContext = createContext(defaultValue).
- Pass it to the useContext(MyContext) Hook to read it in any child component, no matter how deep.
- Wrap children into <MyContext.Provider value={…}> to provide it from a parent.
- Context passes through any components in the middle.
- Context lets you write components that “adapt to their surroundings”.
- Before you use context, try passing props or passing JSX as children.
Responding to Events
- React lets you add event handlers to your JSX. Event handlers are your own functions that will be triggered in response to interactions like clicking, hovering, focusing form inputs, and so on.
- You can handle events by passing a function as a prop to an element like
<button>. - Event handlers must be passed, not called!
onClick={handleClick}, notonClick={handleClick()}. - You can define an event handler function separately or inline.
- Event handlers are defined inside a component, so they can access props.
- You can declare an event handler in a parent and pass it as a prop to a child.
- You can define your own event handler props with application-specific names.
- Events propagate upwards. Call
e.stopPropagation()on the first argument to prevent that. - Events may have unwanted default browser behavior. Call
e.preventDefault()to prevent that. - Explicitly calling an event handler prop from a child handler is a good alternative to propagation.



































![[React]: 컴포넌트간 데이터 전달 (with Props)](/images/react_logo.png)
