Table of Contents
클래스
- 자바스크립트는 클래스가 필요없는 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 언어다
- ES6부터 자바나 C#과 같은 클래스 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어와 매우 유사한 객체 생성 메커니즘을 제공해줬다
- 그리고 타입스크립트에서는 여기에
public,private과 같은 접근 제어자와 추상 클래스, 인터페이스를 추가로 도입했다
클래스 생성
- 클래스를 하나 만들어보자
- 클래스는 타입(
type), 인터페이스(interface) 처럼 객체 타입을 정의하는 것을 넘어, 인스턴스를 생성하는 생성자 역할을 할 수 있다는 점이 클래스만의 특징이다
class Car {
color: string
velocity: number
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
}
const car: Car = new Car('red', 50);
- 주의할 점은, 타입 어노테이션에
Car를 붙이면 이는 클래스Car가 아니라, 객체new Car()를 의미한다는 것이다
const getInstanceFunc = (car: Car) => {
console.log(car)
}
const getClassFunc = (car: typeof Car) => {
console.log(car)
}
getInstanceFunc(car)
getClassFunc(Car)
클래스 상속
- 타입스크립트에서는 자바스크립트에서 제공하는
extends와, 타입스크립트에서 제공하는implements방식으로 상속 관계를 정의할 수 있다 extends는 자바스크립트로 변환된 후에도 남아있지만,implements는 자바스크립트로 변환된 후에는 사라진다- 클래스 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍에서 인터페이스는 의존 관계를 나타내는 역할, 클래스는 실제 객체를 생성하는 구현체 역할을 한다
- (추상적 형태인 인터페이스로 관계를 나타냄으로써 최대한 의존 관계를 느슨하게 만들어준다)
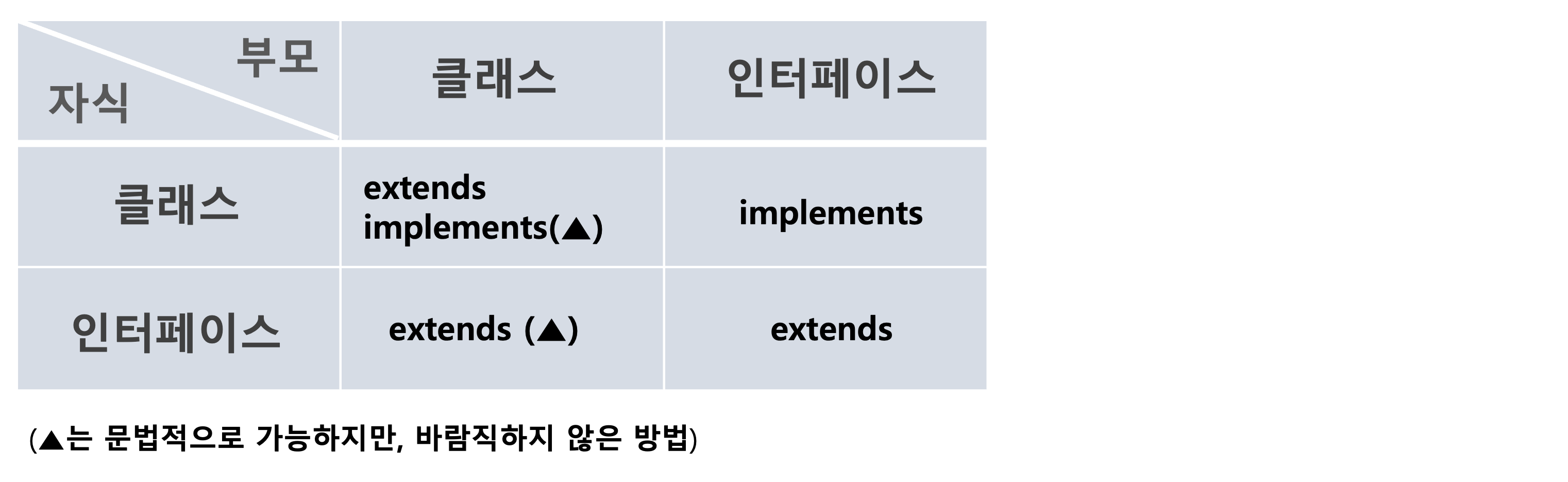
extends
extends는 클래스와 클래스간의 상속 관계 또는 인터페이스와 인터페이스간의 상속 관계를 정의할 때 사용한다
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
}
const hCar: HyundaiCar = new HyundaiCar('red', 50, 120);
HyundaiCar는Car를 상속받기 때문에,Car로서 갖춰야 할 것들은 모두 갖추고 있다. 그래서 타입 어노테이션을Car로 해도 괜찮다
const hCar: Car = new HyundaiCar('black', 50, 130);
- 인터페이스간의 상속 관계도 나타낼 수 있다
interface Car {
color: string
velocity: number
}
interface HyundaiCar extends Car {
color: string
velocity: number
maxVelocity: number
}
implements
Car를 인터페이스로 만든 경우implements를 사용해야 한다- 인터페이스는 구현체가 자신의 속성을 모두 구현(implement)하도록 유도한다
implements는 타입스크립트에서 제공하는 기능이기 때문에 자바스크립트로 변환시 사라진다
interface Car {
color: string
velocity: number
}
class HyundaiCar implements Car {
color: string
velocity: number
maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
this.color = color
this.velocity = velocity
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
}
- 타입 어노테이션을
Car,HyundaiCar어떤 것으로 해도 가능하다
const hCar: HyundaiCar = new HyundaiCar('black', 50, 130);
const hCarTwo: Car = new HyundaiCar('red', 50, 160);
abstract
- 추상클래스는 클래스지만 인터페이스와 유사하다
- 인스턴스 생성 역할을 못한다
- 어떤 클래스가 구현할 때 만족했으면 하는 최소한의 부분을 정의한 클래스
- 추상 클래스는 특정 부분만 구현하도록 요구할 수 있고, 인터페이스는 모든 부분을 구현하도록 요구한다
- 구체적으로 구현해줬으면 하는 요소(프로퍼티, 메서드) 앞에
abstract를 붙여준다
abstract class Car {
color: string
velocity: number
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
abstract printMaxVelocity(): void
}
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
readonly maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
printMaxVelocity(): void {
console.log(this.maxVelocity)
}
}
const car: HyundaiCar = new HyundaiCar('red', 50, 120)
접근 제어자
- 특정 프로퍼티나 메서드의 접근 가능한 정도를 제어할 수 있다 (접근 가능하다는 의미는 get, set 가능하다는 의미)
public,private,protected,readonly는 타입스크립트에만 있다- (자바스크립트에서는
private은#으로 문법적 지원,protected는_로 암묵적 약속으로 사용하고 있었다)
public
- 자기 자신 클래스 뿐만 아니라 어디서든 접근 가능한 프로퍼티 혹은 메서드
- 앞에 아무런 접근 제어자 안붙이면 기본적으로
public이다
class Car {
color: string
velocity: number
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
}
const car: Car = new Car('red', 50)
- 외부에서 읽기/쓰기 가능하다
console.log(car.color)
hCar.color = 'black'
private
- 자기 자신 클래스에서만 접근 가능하다
- 외부에서는 접근 불가능하다. 즉 값을 읽을수도 쓸 수도 없다
class Car {
color: string
private velocity: number
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
}
const car: Car = new Car('red', 50)
velocity는private때문에 외부에서 접근 불가능하다
console.log(car.velocity) // 'velocity' 속성은 private이며 'Car' 클래스 내에서만 액세스할 수 있습니다
- 만약
Car를 상속받는HyundaiCar클래스가 있으면,HyundaiCar의velocity프로퍼티도private이다
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
}
const car: HyundaiCar = new HyundaiCar('red', 50, 120)
car.velocity // 'velocity' 속성은 private이며 'Car' 클래스 내에서만 액세스할 수 있습니다.
protected
- 자신을 상속받은 클래스에서만 접근 가능하다
- 자식 클래스에게만 쓰고 읽을 권한을 준다
class Car {
color: string
private velocity: number // private한 경우
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
}
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
printVelocity() {
console.log(this.velocity) // 'velocity' 속성은 private이며 'Car' 클래스 내에서만 액세스할 수 있습니다.
}
}
class Car {
color: string
protected velocity: number // protected한 경우
constructor(c: string, v: number) {
this.color = c
this.velocity = v
}
}
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
printVelocity() {
console.log(this.velocity) // 자식 클래스에서 접근 가능하다
}
}
readonly
- 내부, 외부에서 모두 쓰기는 불가능하고, 읽기만 가능하다
readonly가 붙은 프로퍼티는 정의와 동시에 할당하거나, 생성자 함수 (constructor) 안에서만 값을 할당할 수 있다
class HyundaiCar extends Car {
readonly maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
super(color, velocity)
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
upgradeMaxVelocity(inc: number) {
console.log(this.maxVelocity) // 이렇게 읽는것만 하는 것은 가능
this.maxVelocity += inc // 쓰기는 불가능 (읽기 전용 속성이므로 'maxVelocity'에 할당할 수 없습니다.)
}
}
const car: HyundaiCar = new HyundaiCar('red', 50, 120)
인터페이스와 접근제어자
- 인터페이스에서는
private,protected같은 것들을 쓸 수 없다 - 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스가 있다고 해보자
- 만약 클래스의 특정 요소에 private을 붙이고 싶다면?
- 클래스에서만
private을 붙이니까, 똑바로 구현을 안했다고 한다. 그래서 인터페이스에도private을 붙이니까 인터페이스에는private을 못 쓴다고 한다
interface Car {
color: string
private velocity: number // 'private' 한정자는 형식 멤버에 나타날 수 없습니다
}
// HyundaiCar' 클래스가 'Car' 인터페이스를 잘못 구현합니다. 'velocity' 속성은 'HyundaiCar' 형식에서 private이지만 'Car' 형식에서는 그렇지 않습니다.
class HyundaiCar implements Car {
color: string
private velocity: number
private maxVelocity: number
constructor(color: string, velocity: number, maxVelocity: number) {
this.color = color
this.velocity = velocity
this.maxVelocity = maxVelocity
}
}
private같은 접근 제어자 쓰고 싶은 경우에는, 인터페이스가 아닌 클래스에 따로 정의 (ex.maxVelocity)- 아니면 추상클래스 사용



































![[Typescript] 클래스 기반의 객체지향 프로그래밍](/images/typescript_logo.png)
