Table of Contents
데이터 준비
- kaggle에서 Cat and Dog 데이터 셋을 다운 받는다
- 나는 아래와 같이 개(dog)와 고양이(cat) 사진을 하나의 폴더에 같이 넣었다
- 입력은 사진이 되고, 정답 레이블은 파일명에서 추출해서 cat을 0으로, dog를 1로 할 것이다
코드
주피터 랩 접속
# 가상환경 활성화
source ~/virtual_environments/deep_learning_macos/bin/activate
# 주피터 랩 접속
jupyter lab
라이브러리 임포트
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
디바이스 선택
- 나는 맥실리콘(M1) 탑재된 맥북으로 코드를 실행하고 있기 때문에, 디바이스로
mps를 선택할 것이다
device = "cpu"
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda:0"
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
device = "mps"
print(device)
- 애플에서 iOS 및 macOS 기기의 GPU를 활용한 컴퓨팅 연산 기능을 제공해주는 프레임워크입니다.
- MPS는 다양한 컨볼루션, 행렬 연산 및 활성화 함수 등과 같은 머신 러닝 연산을 포함한 다양한 그래픽 및 머신 러닝 기능을 제공합니다.
데이터셋 및 데이터로더 만들기
class CustomDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset_dir_path, transform=None):
super().__init__()
self.dataset_dir_path = dataset_dir_path
self.dataset_list = os.listdir(self.dataset_dir_path)
for data in self.dataset_list:
if not data.endswith("jpg"):
self.dataset_list.remove(data)
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_dir_path, self.dataset_list[idx])
image = Image.open(image_path)
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.dataset_list[idx].split(".")[0] == "cat":
label = 0
else:
label = 1
return image, label
train_dataset_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(size=(256, 256)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
test_dataset_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(size=(256, 256)),
transforms.ToTensor()
])
dataset_dir_path = "./dataset"
train_dataset_dir_path = os.path.join (dataset_dir_path, "train")
test_dataset_dir_path = os.path.join (dataset_dir_path, "test")
train_dataset = CustomDataset(train_dataset_dir_path, transform=train_dataset_transforms)
test_dataset = CustomDataset(test_dataset_dir_path, transform=test_dataset_transforms)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
모델
- 직접 모델을 만드는 경우
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, numClass=2):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 16)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 58 * 58, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, numClass)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except batch
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
- pretrained 된 모델을 사용할 경우
from torchvision.models import resnet50, ResNet50_Weights
resnet = resnet50(weights=ResNet50_Weights.DEFAULT)
for param in list(resnet.parameters()):
param.requires_grad=False
resnet.fc = nn.Sequential(resnet.fc, nn.Linear(1000, 2))
- 모델, 옵티마이저, 손실함수를 정의하고, 모델과 손실함수는
.to()메서드를 사용해 GPU 메모리에 올린다
model = resnet
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
model.to(device)
criterion.to(device)
학습
def train():
model.train()
total = 0
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (imgs, labels) in enumerate(train_dataloader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
imgs = imgs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(imgs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total += labels.shape[0]
running_loss += loss.item()
running_corrects += sum(preds == labels)
print(f'train loss: {running_loss / total}, accuracy: {running_corrects / total}')
return running_loss / total, (running_corrects / total).item()
def validate():
model.eval()
total = 0
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (imgs, labels) in enumerate(test_dataloader):
imgs = imgs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(imgs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
total += labels.shape[0]
running_loss += loss.item()
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
print(f'val loss: {running_loss / total}, accuracy: {running_corrects / total}')
return running_loss / total, (running_corrects / total).item()
num_epochs = 5
best_val_acc = 0
best_epoch = 0
history = []
accuracy = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print(f'===========================[Epoch: {epoch + 1}===========================')
train_loss, train_acc = train()
val_loss, val_acc = validate()
history.append((train_loss, val_loss))
accuracy.append((train_acc, val_acc))
if val_acc > best_val_acc:
print("[Info] best validation accuracy!")
best_val_acc = val_acc
best_epoch = epoch
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"best_checkpoint_epoch_{epoch + 1}.pth")
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"last_checkpoint_epoch_{num_epochs}.pth")
plt.plot([x[0] for x in accuracy], 'b', label='train')
plt.plot([x[1] for x in accuracy], 'r--',label='validation')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.legend()
# test_loss, test_accuracy = test()
# print(f"Test loss: {test_loss:.8f}")
# print(f"Test accuracy: {test_accuracy * 100.:.2f}%")
학습 결과 및 추론
- pretrained 모델의 위엄.. 단 한번의 학습에 검증 데이터 셋에서 정확도가 98% 나온다
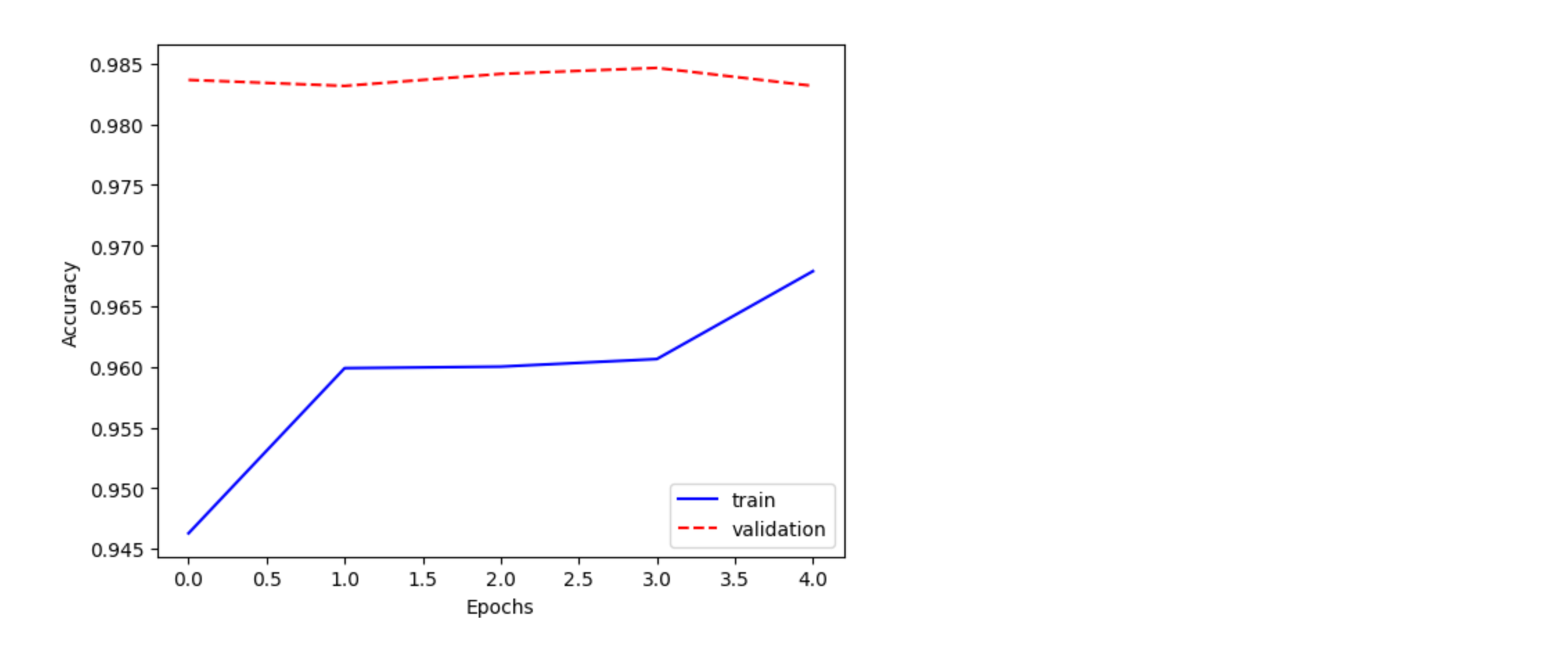
- 추론 결과를 확인해보자
fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(5, 10))
fig.tight_layout()
for inputs, labels in test_dataloader:
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
for idx, (input, pred, label) in enumerate(zip(inputs, preds, labels)):
input = torch.transpose(input, 0, 2)
input = torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)
input_numpy_arr = input.cpu().numpy()
ax[idx].set_title(f"pred: {'Cat' if pred == 0 else 'Dog'}, answer: {'Cat' if label == 0 else 'Dog'}")
ax[idx].imshow(input_numpy_arr)
break

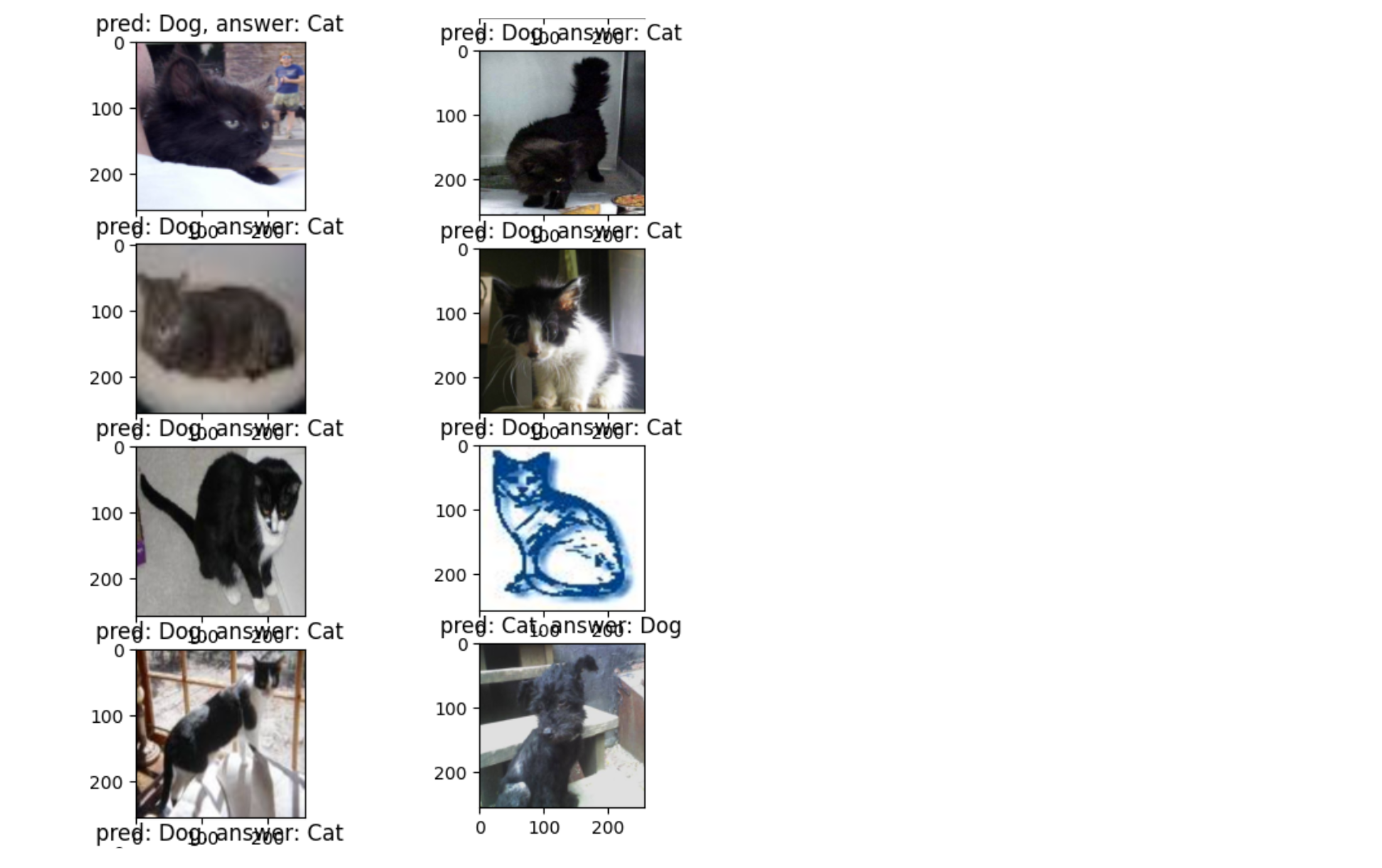
- 모델의 예측이 잘못된 경우만 살펴보자
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(5, 20))
cnt = 1
for inputs, labels in test_dataloader:
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
for idx, (input, pred, label) in enumerate(zip(inputs, preds, labels)):
input = torch.transpose(input, 0, 2)
input = torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)
input_numpy_arr = input.cpu().numpy()
if pred != label:
if cnt == 10:
break
ax = fig.add_subplot(10, 1, cnt)
ax.imshow(input_numpy_arr)
ax.set_title(f"pred: {'Cat' if pred == 0 else 'Dog'}, answer: {'Cat' if label == 0 else 'Dog'}")
cnt += 1
- 털이 검은색인 경우, 화질이 떨어지는 경우 예측을 잘 못한다
- 또 그림체처럼 학습시 잘 못본 데이터의 경우에도 예측을 잘 못하게 된다




































![[Computer Vision] 개, 고양이 이미지 분류](/images/cv_logo.png)
