Table of Contents
Log의 중요성
MySQL은 오픈 소스 관계형 데이터베이스이며 효율성과 보안을 향상시키기 위해 MySQL 데이터베이스 로그를 사용하는 방법을 배워야 한다. 장기적으로 MySQL 인스턴스의 성능을 진단하고 모니터링하는 방법을 이해하는 것이 중요하다.
MySQL을 서비스 단계에서 사용하다 보면 슬로우 쿼리(slow query), 데드락(deadlock), 커넥션 실패(aborted connection)과 같은 문제를 마주하게 된다. 로깅은 이러한 문제를 진단하는데 필수적이다. 또한 로그는 보안 문제를 진단하는데도 사용된다.
MySQL의 로그
MySQL에는 6가지의 로그 타입이 있다.
- Redo log(WAL)
- Undo log
- Binary log
- Error log
- Slow query log
- General log
여기서 Redo log와 Undo log 그리고 Binary log는 트랜잭션 처리와 밀접한 관련이 있는 로그들이다. 다른 로그들은 MySQL 서버를 모니터링 하는데 도움이 되는 로그들이다.
MySQL 모니터링을 위한 로그
위에서 MySQL의 로그를 이용해 슬로우 쿼리, 데드락, 연결 실패, 보안과 관련한 문제들을 진단하는데 도움을 준다고 했다. MySQL의 로그를 모니터링함으로써 이러한 문제를 해결하고 성능을 향상시켜 보자.
모니터링에 사용되는 로그들은 다음과 같다.
- General Query Log
- Slow Query Log
- Error Log
- Binary Log
# 설정값 확인하기
mysql> show variables;
# Enable Logging on MySQL
mysql>SET GLOBAL general_log = ‘ON’;
# Log가 저장되는 파일 경로
mysql>SET GLOBAL general_log_file = ‘path_on_your_system’;
# Enable Logging on MySQL
mysql>SET GLOBAL slow_query_log = ‘ON’;
# Log가 저장되는 파일 경로
mysql>SET GLOBAL slow_query_log_file = ‘path_on_your_system’;
General Query Log
General query log는 서버가 요청받은 명령어들을 기록한다. 예를 들어 클라이언트의 연결/해제 부터해서 클라이언트가 요청한 SQL문도 기록한다. 이 로그를 통해 서버에 에러가 의심될 때 어떤 요청이 들어왔는지 알 수 있다.
General query log에 기록되는 순서는 요청이 들어온 순으로 기록된다. 처리가 완료되지 않았더라도 일단 General query log에 기록된다. 이런 점 때문에 MySQL 서버의 장애를 디버깅하기에 좋은 로그가 된다.
처리되지 않은 요청도 모두 로그에 기록되기 때문에, 로그 파일의 사이즈가 비교적 빨리 커진다. 그래서 만약 데이터에 변화를 준 요청만 기록된 로그를 보고 싶다면 Binary log를 사용하는 것이 낫다.
Slow Query Log
서비스의 규모가 커지게 되면, 빨랐던 쿼리들도 느려지는 일이 발생한다. 이렇게 느린 쿼리 문제를 디버깅할 때에 Slow query log를 사용하는 것이 좋은 출발점이 된다.
Slow query log는 내가 설정한 기준(threshold) 시간을 넘어가는 쿼리 실행문을 저장한다. 디폴트는 10초이다.
# threshold 값 설정하기
SET GLOBAL long_query_time = 5.0;
아래와 같은 쿼리를 실행해서 내가 설정한 대로 제대로 동작하는지 확인해 볼 수도 있다.
SELECT SLEEP(7);
대개 인덱스를 사용하지 못하는 쿼리들이 문제의 대상이 된다. 그래서 만약 log_queries_not_using_indexes 시스템 변수를 ON으로 하면 실행 시간에 상관없이 무조건 Slow query log에 인덱스를 사용하지 않는 실행문을 남길 수 있다.
SHOW variables LIKE 'slow%';
# 슬로우 로그 조회하기
SELECT * FROM mysql.slow_log;
# 또는
SELECT start_time, user_host, query_time, lock_time, rows_sent, rows_examined, db, CONVERT(sql_text USING utf8 ) sql_text
FROM mysql.slow_log;
Error Log
MySQL은 Error log를 사용하여 서버 시작 및 종료 시 그리고 서버가 실행되는 동안 발생하는 진단 메시지, 경고 및 메모를 기록합니다. Error log에는 MySQL 시작 및 종료 시간도 기록됩니다.
Error log는 항상 활성화 되어 있습니다. 만약 Error log 파일 경로를 명시하지 않으면 콘솔에라도 출력하게 됩니다.
보통 에러로그에 많이 저장되는 에러
- Permission errors
- Configuration errors
- Out of memory errors
- Errors with initiation or shutdown of plugins and InnoDB
Binary Log
Binary log는 데이터 또는 스키마에 변경을 일으킨 실행문만 기록한다. 예를 들어 INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE와 같은 실행문은 기록하고, SELECT, SHOW와 같은 실행문은 로그에 기록하지 않는다. Binary 로그는 각 실행문이 실행되는데 얼마나 걸렸는지 기록되어 있다.
Redo log는 트랜잭션 처리를 위한 InnoDB 엔진만의 특별한 존재이다. 그렇다면 다른 스토리지 엔진을 쓰는 경우는 어떻게 할까?
그래서 스토리지 엔진에 상관없이 MySQL Server레벨에서 가지는 로그가 있는데 그게 바로 Binary log이다.
Binary log는 General query log와 다르게, 실행문이 만들어낸 변화가 커밋되었을 떄 Binary log에 기록된다.
Binary log는 말그대로 바이너리 포맷으로 저장된다, 그래서 Binary log를 읽으려면 mysqlbinlog 유틸리티를 사용해야 한다.
아래는 Binary log binlog.0000001을 읽을 수 있는 방법을 소개한다.
mysql> mysqlbinlog binlog.0000001
MySQL은 Binary log가 로깅될 때 크게 3가지 포맷을 제공한다.
- Statement-based logging: In this format, MySQL records the SQL statements that produce data changes. Statement-based logging is useful when many rows are affected by an event because it is more efficient to log a few statements than many rows.
- Row-based logging: In this format, changes to individual rows are recorded instead of the SQL statements. This is useful for queries that require a lot of execution time on the source but result in just a few rows being modified.
- Mixed logging: This is the recommended logging format. It uses statement-based logging by default but switches to row-based logging when required.
런타임이나 복제가 진행 중일 때는 Binary log 포맷을 바꾸지 않는 것이 좋다. 아래는 바꾸는 코드다.
SET GLOBAL binlog_format = 'STATEMENT';
SET GLOBAL binlog_format = 'ROW';
SET GLOBAL binlog_format = 'MIXED';
트랜잭션 처리를 위한 로그
데이터베이스는 보통 트랜잭션 수행을 위해 로그를 사용한다. 보통 이러한 역할을 수행하는 로그를 트랜잭션 로그라고 하며 MySQL의 경우 Redo Log, Undo Log, Binary Log가 이에 해당한다. Undo Log는 트랜잭션의 Atomicity, Redo Log는 Durability를 제공해준다.
MySQL은 디스크의 I/O으로 인한 성능 저하를 줄이기 위해 캐싱 메커니즘을 사용한다.
데이터베이스를 수정하는 쿼리가 들어오면, InnoDB는 먼저 메모리에 데이터가 있는지 확인하고, 없으면 디스크에서 불러와 메모리에 올리고 데이터를 수정한다. 이렇게 메모리에서만 계속 읽고 쓰게되면 장애로 서버가 종료될 때 데이터가 날아가게 된다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 MySQL에서는 Redo Log를 사용한다. 더 자세한 내용은 밑에서 살펴볼 것이다. 또한 데이터 수정 쿼리가 들어올 때마다 메모리의 데이터를 바로 수정하지는 않고, 이 전 값을 Undo Log에 보관해두고 수정을 가함으로써, 트랜잭션이 실패할 경우 데이터를 롤백(Roll back)할 준비를 한다. 이 내용도 밑에서 더 자세히 살펴보자.
(참고로 디스크에 있는 파일중 데이터를 저장하는 파일을 데이터 파일, 로그를 저장하를 파일을 로그 파일이라고 함)
(메모리에 있는 버퍼중 데이터 페이지를 캐시해놓는 위치를 데이터 버퍼, 로그를 캐시해놓는 위치를 로그 버퍼라고 함)
(InnoDB엔진이 데이터를 읽고 쓸 때는 해당하는 데이터와 인덱스를 메모리 버퍼 풀에 올려둔다.)
Memory Buffer pool: occupies the largest block of memory. The cache used to store various data includes index pages, data pages, undo pages, insert buffers, adaptive hash indexes, lock information stored in innodb, data dictionary information, etc. The working method always reads the database file into the buffer pool by page (16k per page), and then retains the cached data in the buffer pool according to the least recently used (lru) algorithm. If the database file needs to be modified, always modify the page in the buffer pool first (dirty page after the modification occurs), and then flush the dirty page of the buffer pool to the file at a certain frequency.
Undo Log
Undo log is to achieve atomicity of transactions. Undo Log is also used to implement multi-version concurrency control (referred to as: MVCC).
- Undo log는 트랜잭션의 Atomicity 특성을 지키기 위한 로그
- Undo log는 MVCC(multi-version concurrency control)를 위해서도 사용
Undo log는 Undo log file이라는 파일이 따로 없고, Table space라는 공간의 일부인 Undo segment라는 곳에 저장된다.
Delete/Update 작업의 내부 메커니즘
Undo log의 원리는 굉장히 간단하다. 트랜잭션의 원자적 특성을 지키기 위해, 어떤 작업을 하려는 데이터는 그 전에 먼저 데이터를 Undo log에 백업해둔다. 그리고 난 후 Delete/Update한다. 만약 중간에 장애가 발생하거나, ROLLBACK이 일어나면 Undo log를 이용해 트랜잭션이 발생하기 전 데이터로 돌아갈 수 있다.
예를 들어 A=1과 B=2인 데이터가 있을 떄 각각 +2를 하는 작업을 수행한다고 해보자.
- Record A=1 to undo log.
- Modify A=3.
- Record B=2 to undo log.
- Modify B=4.
----------------------------------
- Write undo log to disk.
- Write data to disk.
여기서 중요한 점은,
- 데이터를 변경하기 전에 먼저 Undo log에 기록해둔다.
- 데이터를 커밋하기 전에 먼저 Undo log를 Log buffer에서 Undo segment로 flush한다.
Redo Log
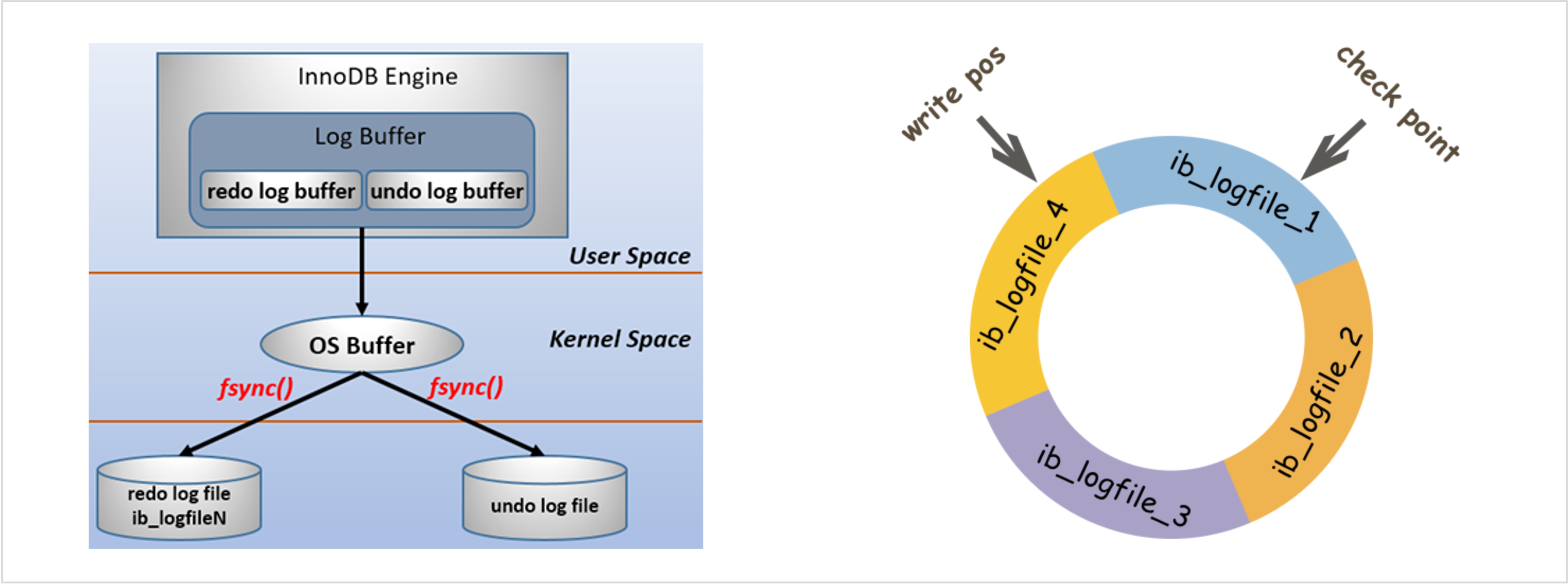
Redo log는 실행된 SQL문을 저장하기 위한 파일이다. 만약 MySQL 서버에 장애가 발생했다면 Redo log에 저장된 SQL문을 재실행 함으로써 원하는 데이터 상태를 다시 얻을 수 있다.
The redo log exists as a separate file on the disk. There will be two files by default, named ib_logfile0 and ib_logfile1.
innodb_log_file_size: the size of the redo loginnodb_log_file_in_group specifies: the number of the redo log, and the default is 2innodb_log_group_home_dir: the path where the redo log is located
innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 100M
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
innodb_data_home_dir =/home/mysql/local/mysql/var
innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:1G: autoextend
innodb_file_io_threads = 4
innodb_thread_concurrency = 16
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1
innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M
innodb_log_file_size = 128M
innodb_log_file_in_group = 2
innodb_log_group_home_dir =/home/mysql/local/mysql/var
InnoDB는 Undo log의 작업(operation)을 Redo log의 로그로 기록한다. 그러면 Undo log를 자주 flush 하지 않아도 된다. Redo log에 기록되었기 때문에. Redo log만 자주 flush해주면 된다.
데이터 변경 작업이 일어날 때 하는 Undo log의 행동(Undo log를 기록한다, 데이터를 변경한다)들을 하나의 실행문으로 생각하고 Redo log에 저장해둔다.
Redo log의 I/O 퍼포먼스
데이터 작업은 최대한 메모리 위에 있는 페이지에서 하고, 디스크로 flush하는 작업은 DB의 리소스가 여유로울 때 하는 것이 좋다. 그래서 메모리 버퍼 풀을 이용하는 것이다. 근데 그러면 장애 발생으로 서버가 종료될 때 문제가 된다.
그래서 복구가 가능하도록 하기 위해 등장한 것이 Redo log이고, 중간중간 Redo log만 Log buffer에서 Log file로 flush함으로써 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
여기서 드는 생각은 “성능 저하의 주요 요인이 디스크로 flush하는 작업이었는데, Redo log를 디스크로 flush하면 결국 달라지는 게 없지 않는가?”라는 점이다.
하지만 디스크 작업에도 비교적 빠른 작업이 있고, 느린 작업이 있다. 빠른 작업은 디스크의 내용을 순차적으로 읽는 Sequential Access, 느린 작업은 디스크의 블럭을 자주 옮겨 다녀야 하는 Random Access이다.
다시 Redo log로 돌아와보면, Redo log는 디스크의 Log file에 단순히 SQL statement를 append하는 형식이다. 그래서 이 작업은 Sequential Access에 해당한다. 하지만 데이터를 디스크로 flush하는 작업은 디스크 내의 데이터 위치를 찾아야 하기 때문에 Random Access가 발생한다. 이것이 바로 Redo log를 사용하는 것이 더 빠른 이유다.
트랜잭션 처리시 일어나는 Undo log와 Redo log의 작업
1. Transaction start.
2. Record A=1 to undo log.
3. Modify A=3.
4. Record 2, 3 to redo log.
5. Record B=2 to undo log.
6. Modify B=4.
7. Record 5, 6 to redo log.
8. Write redo log to disk.
9. Transaction commit
한 가지 알아야 할 점은 Redo log가 있다고 하더라도, 트랜잭션 한 번마다 Redo log가 flush되는게 아니라면 데이터 손실은 피할 수 없다. 그렇기 때문에 은행과 같이 데이터 손실이 하나라도 발생해서는 안되는 곳에서는 트랜잭션 하나를 완료하기 전에 무조건 디스크로 Redo log를 flush하고 커밋을 하게 된다. (트랜잭션 한 개 마다 Redo log flush)
the role of redo & undo log
- Data persistence
- The buffer pool maintains a linked list in the order of dirty page modification, called flush_list. Flush data to persistent storage according to the order of pages in flush_list. The pages are arranged in the order of the earliest modification. Under normal circumstances, when is the dirty page flushed to the disk?
- When the redo space is full, part of the dirty page will be flushed to the disk, and then part of the redo log will be released.
- When you need to allocate a page in the Buffer pool, but it is full, you must flush dirty pages to disk. Generally, this situation can be controlled by the startup parameter innodb_max_dirty_pages_pct. When the dirty page in the buffer pool reaches this ratio, the dirty page is flushed to the disk.
- When the system is detected to be idle, it will flush.
- The buffer pool maintains a linked list in the order of dirty page modification, called flush_list. Flush data to persistent storage according to the order of pages in flush_list. The pages are arranged in the order of the earliest modification. Under normal circumstances, when is the dirty page flushed to the disk?
- Data Recovery
- Over time, Redo Log will become very large. If you start to recover from the first record every time, the recovery process will be very slow and cannot be tolerated. In order to reduce the recovery time, the Checkpoint mechanism is introduced. Suppose that at a certain point in time, all dirty pages have been flushed to disk. All Redo Logs before this time point do not need to be redone. The system records the end of the redo log at this point in time as the checkpoint. When restoring, just start from this checkpoint position. The log before the checkpoint point is no longer needed and can be deleted.
Binary Log
- Redo log는 트랜잭션 처리를 위한 InnoDB 엔진만의 특별한 존재이다. 그렇다면 다른 스토리지 엔진을 쓰는 경우는 어떻게 할까?
- 그래서 스토리지 엔진에 상관없이 MySQL Server레벨에서 가지는 로그가 있는데 그게 바로 Binry log이다.
- Binary log는 스키마, 테이블에 관한 모든 변경 항을 기록한다. (SELECT와 SHOW 쿼리는 X)
- Binary log는 실행문의 실행 시간도 기록해둔다.
Redo log와 Binary log
- The content is different: redo log is a physical log and the content is based on the Page on disk, bin-log content is binary and depending on the binlog_format parameter, may be based on SQL statements, on the data itself, or a mixture of the two.
- Different levels: redo log works with InnoDB and the engine, bin-log is located at the MySQL Server level and is available to all engines.
- Different forms of disk storage: redo log writes cyclically, bin-log accumulates, so it can be used for data recovery or primary-secondary synchronization
- The timing of writing is different: bin-log are written when a transaction usually commits or when N transactions commit once, redo log are written at a variety of times, either every time a transaction commits, by another threaded transaction, or every second when the disk is flushed. (Note: uncommitted transactions in redo log may also be flushed to disk)
- Different roles: redo log is used for crash recovery to ensure that MySQL downtime does not affect persistence; bin-log is used for point-in-time recovery to ensure that the server can recover data based on the point in time, in addition bin-log is also used for primary-secondary replication.
Two-phase Commit
Because redo-log is in the InnoDB tier and bin-log is in the Server tier, this introduces a new problem.
If the redo log is written successfully and the bin-log crashes before it is written to disk, the transaction has not yet been committed, so the new data written to the redo-log is invalid.
Restarting the database for data recovery restores the data in the redo-log to disk, which creates invalid data.
In this case, as you wisely know, a two-phase commit is introduced.
- In the first stage, the redo-log is written and in the prepared state.
- After the Server layer saves the bin-log data and drops it to disk, the transaction commits the redo-log at the same time, so that the redo-log becomes committed, which ensures the consistency of the redo-log data and the bin-log data.
Update문 실행 예제
With the previous knowledge, you can now explore how the update statement is executed in MySQL.
Suppose we now execute the SQL : update table_test set a = a+1 where id = 2;
- First, the client connects via the connector and determines the permissions.
- After verification, the SQL goes through the parser for lexical and syntax analysis (AST) and if it is an Update statement, MySQL will clear all the query cache for the query table table_test. (As you can see, it is not recommended to turn on the query cache)
- The optimizer optimizes the validated SQL, plans to match the id index, and generates an execution plan.
- The executor gets the final SQL and calls the interface of the corresponding storage engine to start executing the update SQL.
- The InnoDB engine opens a transaction, the execution engine first queries from memory whether there is data with id=2, if it matches then the corresponding data with field+1, and then saves it to memory. If it does not query the data with id=2 then it will go to the disk, the query will read the data into memory in pages, then update it and save it to memory.
- The InnoDB engine will then save the data rows to redo-log, which is pre-committed, notifying the Server’s executor that it is ready to commit the transaction.
- The executor will generate the corresponding bin-log and write it to disk.
- The transaction is committed and the redo-log is then committed.
- This is where the execution of a transaction is complete.
참고
- 해커의 개발일기, 데이터베이스의 무결성을 보장해주는 Write-Ahead-Log
- alibabacloud, What are the Differences and Functions of the Redo Log, Undo Log, and Binlog in MySQL?
- Coralogix, 5 Essential MySQL Database Logs To Keep an Eye On
- scaling.dev, Transaction Log. Commit Log. WAL.
- PostgreSQL 공식문서, Write-Ahead Logging (WAL)
- Dwen, MySQL’s RedoLog and BinLog
- developPAPER, You must understand the three MySQL logs – binlog, redo log and undo log
- MySQL 공식문서, 14.6.6 Redo Log
- Katastros, InnoDB transaction log (redo log and undo log) detailed
- heesuk-ahn, [데이터베이스] binary log 란?
- The Binary Log
- Log-structured storage
- ghyeong, 슬로우 쿼리(Slow Query) 조회 쿼리(Oracle, MS-SQL, Mysql, postgreSQL)
- MySQL 공식문서, The Slow Query Log



































![[MySQL] MySQL의 로그 (이론)](/images/mysql_logo.png)
